Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Engineering, Xi’an University of Post & Telecommunications, Xi’an 710121, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
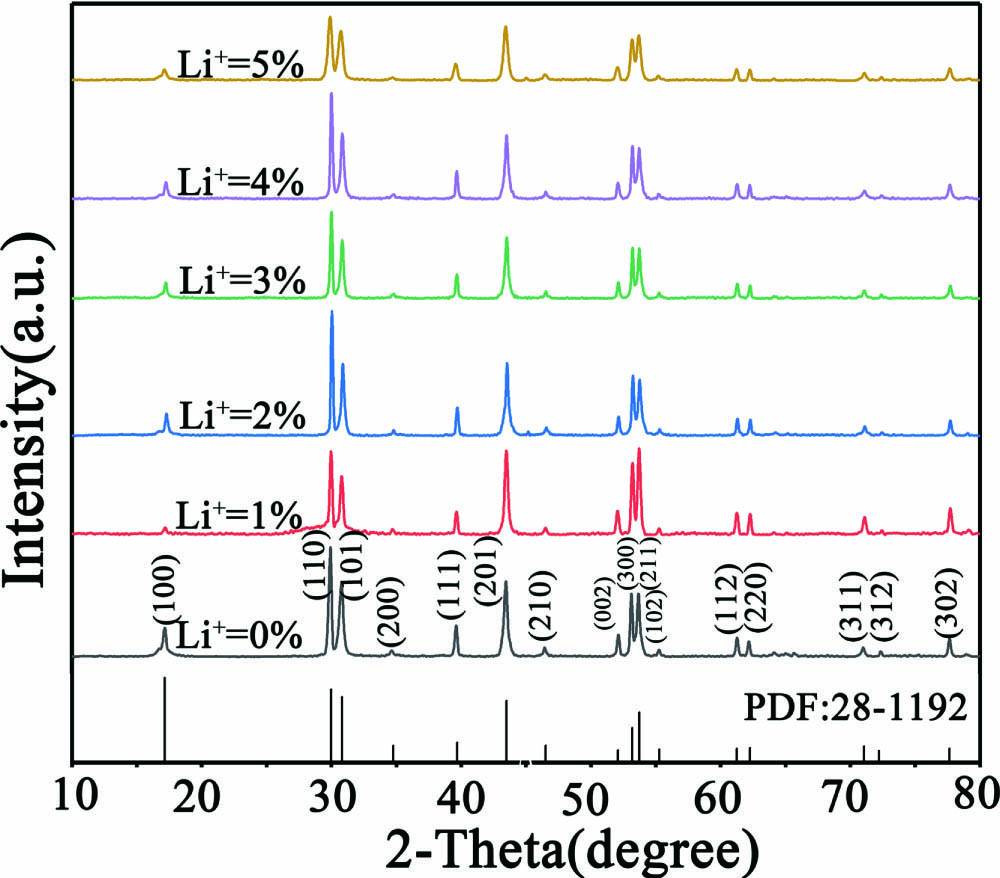
Li ions affect the upconversion efficiency by changing the local crystal field of the luminescent center. Herein, in order to improve the upconversion efficiency of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+, a series of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ micro-particles with different Li+ doping concentrations were synthesized by the hydrothermal synthesis method, respectively. Firstly, the structure and morphology of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ upconversion micro-particles (UCMPs) with different doping concentrations were analyzed by X-ray diffraction and a scanning electron microscope (SEM). SEM results show that the UCMPs are not only highly crystallized, but also have hexagons with different Li+ concentrations of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+. X-ray diffraction shows that the crystal field around Eu3+ changes with the increase of Li+ concentration. Then, the fluorescence spectrum of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ was studied under the irradiation of a 980 nm laser. The results show that the fluorescence intensity of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ with 2% Li+ is the strongest, which is twice the intensity of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ without Li+. Finally, the fluorescence imaging analysis of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ with 2% Li+ concentration was carried out. The UCMPs are used to screen printing to evaluate the imaging effect on different sample surfaces. The results show NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ (with 2% Li+) has great application prospects in anti-counterfeiting recognition.
upconversion micro-particles hydrothermal synthesis anti-counterfeiting identification screen printing Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(11): 110501
1 西安邮电大学 电子工程学院, 陕西 西安 710121
2 西安邮电大学 理学院, 陕西 西安 710121
采用COMSOL有限元分析软件的固体传热模块, 对有机电致发光器件(OLED)的热学特性进行了仿真, 发现器件温度随着输入功率成线性增大。在驱动电流为150 mA·cm-2时, 仿真结果表明, Alq3发光层的最高温度为82.994 3 ℃; 玻璃基板下表面的最高温是77.392 6 ℃; 器件阴极表面中心区域的最高温度为82.994 2 ℃, 其平均温度为78.445 ℃。通过改变功能层热传导率、功能层厚度、对流换热系数、表面发射率等参数模拟其对OLED器件热学特性的影响, 结果表明, 当增加基板的热传导率时, OLED器件温度显著下降而且表面及内部温度梯度大幅减小; 提高空气对流换热系数及基板的表面发射率, OLED的温度可以大幅减小。而其他参数则对其影响并不明显。
有机电致发光器件 有限元分析 温度分布 热学特性 散热 organic light emitting device finite element analysis temperature distribution thermal characteristics thermal dissipation 红外与激光工程
2018, 47(7): 0720001





